| Table of Contents | ||
|---|---|---|
|
The C3 AI Suite provides researchers many tools to analyze data and build and deploy machine learning models. This guide explains how to connect to a C3.ai clusterthe C3 AI Suite, access data using C3 .ai AI methods, and convert C3 .ai AI method outputs to an easy-to-analyze form. Additionally, the guide also provides more detailed instructions to DTI members using the Covid-19 DataLakeData Lake. Examples in this guide work using the base Datalake rely on the 'baseCovidDataLake' package available in the this git repository: https://github.com/c3aidti/dtiTraining
Please note, this guide covers how to run read-only queries on query data from the C3 AI Suite. For more advanced topics , such as loading data, building metrics, or configuring and training machine learning models, please refer to the following wikis:
- Data Integration (Not yet available)
- Metrics (Not yet available)
- Machine Learning (Not yet available)
Terminology
To best understand the C3 AI Suite and this guide, welet're going to s introduce some key terminology used throughout the suite.by C3 AI Suite developers:
- Type: Everything within Nearly all aspects of the C3 AI Suite is stored and (e.g., data, machine learning models, cloud-provider microservices) are stored and accessed through Types. These C3 AI Types are logical objects akin to a Java class which , and contain 'fields' and 'methods'. Some Types are persisted to internal databases , and (like Postgres or Cassandra), while others are not. Nearly every aspect of the C3 AI Suite is accessed through Types.
- Field: A field of a C3 Type. This contains Fields contain attributes or data associated with the Type.
- Method: A method defined declared on a C3 Type. Methods define business logic associated with the Type.
- Vanity Url: The URL at which a specific tenant/tag of a C3 Cluster can be accessed. The C3 Cluster itself has a URL as well, however most interaction with
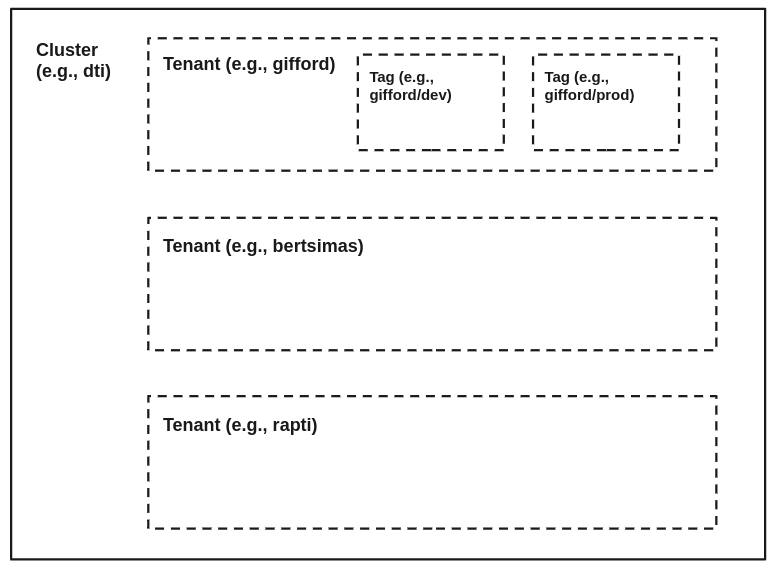
- Cluster: A deployment of the C3 AI Suite is done through the vanity url.Cluster: A deployment of the C3 AI Suite. This can exist in the cloud or in a container. A C3 Cluster is a collection of hardware or virtualized cloud instances (e.g., servers, databases, load balancers) used to run the C3 AI Suite and C3 AI Applications. The C3 AI Suite is capable of running on top of numerous tehnologies such as different cloud providers, or virtualization strategiescan run on any public or private cloud infrastructure or on a local machine (in a docker container).
- Tenant: A logical partition of a C3 Cluster. While internally, some data between Tenants may be stored on the same database, this access is not extended to Users of the C3 AI Suite. Users All tenants in a cluster generally share the same compute and storage resources. Data within tenants, while stored in a single database, are logically separated. C3 AI Suite users on one tenant can't see data stored on another Tenanttenant. In other words, users are only able to view data for tenants to which they are explicitly granted access.
- Tag: A slot on which a C3 package is run. Tags sit within a Tenant.logical partition of a tenant. A single tag hosts one C3 AI application (deployed package).
- Package: All the code a developer writes for an application. The Package: The code which the C3 AI Suite runs a package on a Tag. This is what the developer edits.tag.
- Provisioning: The loading Deploying a Package package onto a tenant/tag in a C3 Tenant/TagCluster.
- Static Console: The main method C3 A browser-based tool that C3 AI developers use to interact with their the C3 Tag. You can access the static console at the url 'https://AI Suite. Static console is available on all modern browsers, including Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Apple Safari. Developers use the console to query data, evaluate expressions, view documentation, monitor environments, develop and test code, and manage environment configurations. You can access the static console at the url '
https://<vanity_url>/static/console' (Replace replacing<vanity_url>with your vanity urlVanity Url).) - Metric: A data analysis object which turns timeseries-like data into a timeseries.Expressions that transform raw data into a time-series.
C3 Cluster Overview
The C3 AI Suite is a Platform as a Service (PaaS) system which can exist on top of a number of virtualization technologies and platforms. Generally, A C3 Cluster consists of one or more master nodes which orchestrate jobs which need to be completed, worker nodes that carry out scheduled tasks, and finally some nodes dedicated to technologies on which the platform is based such as postgres and cassandra. On top of this physical computational structure sits a logical software structure which is starts at the top level of Cluster, then Tenant, then Tag. Each cluster contains Tenants which are logically separated from each other (e.g., Packages run on separate Tenants cannot view data from eachother), and each Tenant contains Tags. Tags house C3 Packages which are the actual code that C3 developers provision to the platform. A typical Multi-user Multi, which enables organizations to build, deploy, and operate enterprise-scale Big Data, AI, and IoT applications. The C3 AI Suite can be deployed on any private or public cloud infrastructure such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. When developing and operating applications, a C3 cluster is responsible for managing and supporting all the features of the C3 AI Suite. A C3 Cluster has at least one Master node and many Worker nodes. Master nodes prioritize and distribute jobs to Worker nodes and handle user requests. Worker nodes carry out jobs, allocated by the Master node. Other components of a C3 Cluster include databases (e.g., Postgres, Cassandra, Azure Blob), logging services (i.e., Splunk), and Jupyter. Atop these hardware or virtualized cloud resources is a logical software structure, with the highest level being a Cluster. A C3 Cluster is broken out into numerous tenants. Tenants are logically separated from each other (i.e., a particular tenant's data and packages are not accessible or visible to any other tenants), and contain many tags. Tags host C3 AI Packages (i.e., the code that C3 AI developers write and provision to the C3 AI Suite). A typical multi-tag, multi-tenant C3 Cluster is shown in a logical diagram below:
To learn more about the general structure architecture of a C3 cluster, please see the C3.ai resources training materials here:
- Developer Documentation
- C3.ai Academy Videoshttps:
- //learnc3.litmos.com/course/3802332/module/7466213/Scorm?LPId=118058&Review=False&Reattempt=True
- Packages
- Clusters, Tenants, and Tags
Provision a C3 AI Package
Provision your C3 To provision a package to your C3 cluster/tenant/tag following tag, follow the instructions available at the DTI Guide: Provisioning Guide.
To run . DTI members wishing to execute the examples in this guide should you will need to provision the 'baseCovidDataLake' by following the directions under in the heading 'COVID-19 DataLake Data Lake Provisioning' section.
To learn more about the general structure of a C3 clusterprovisioning, please see the C3 .ai resources AI Develop Documentation here:
- Developer Documentation
- C3.ai Academy Videoshttps://learnc3.litmos.com/course/3802332/module/7466213/Scorm?LPId=118058&Review=False&Reattempt=True
- Provisioning
Connecting to
...
the C3 AI Suite
The static console is the main location from which C3 developers typically configure and tool that developers use to interact with the C3 AI Suite. We However, we anticipate however, that most DTI researchers members will use Python (via Jupyter notebook) for data analysis. That being said, the static console is an essential component part of working with the C3 AI Suite , and you will use it frequently. For example, the static console is the best place to find documentation tailored directly to your C3 Package. Its package. It's also a great place to quickly test some queries since as no specialized environments need to be set up to use it. It's ready to go in your browserStatic console is ready-to-go in all modern browsers, including Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Apple Safari.
Accessing the Static Console
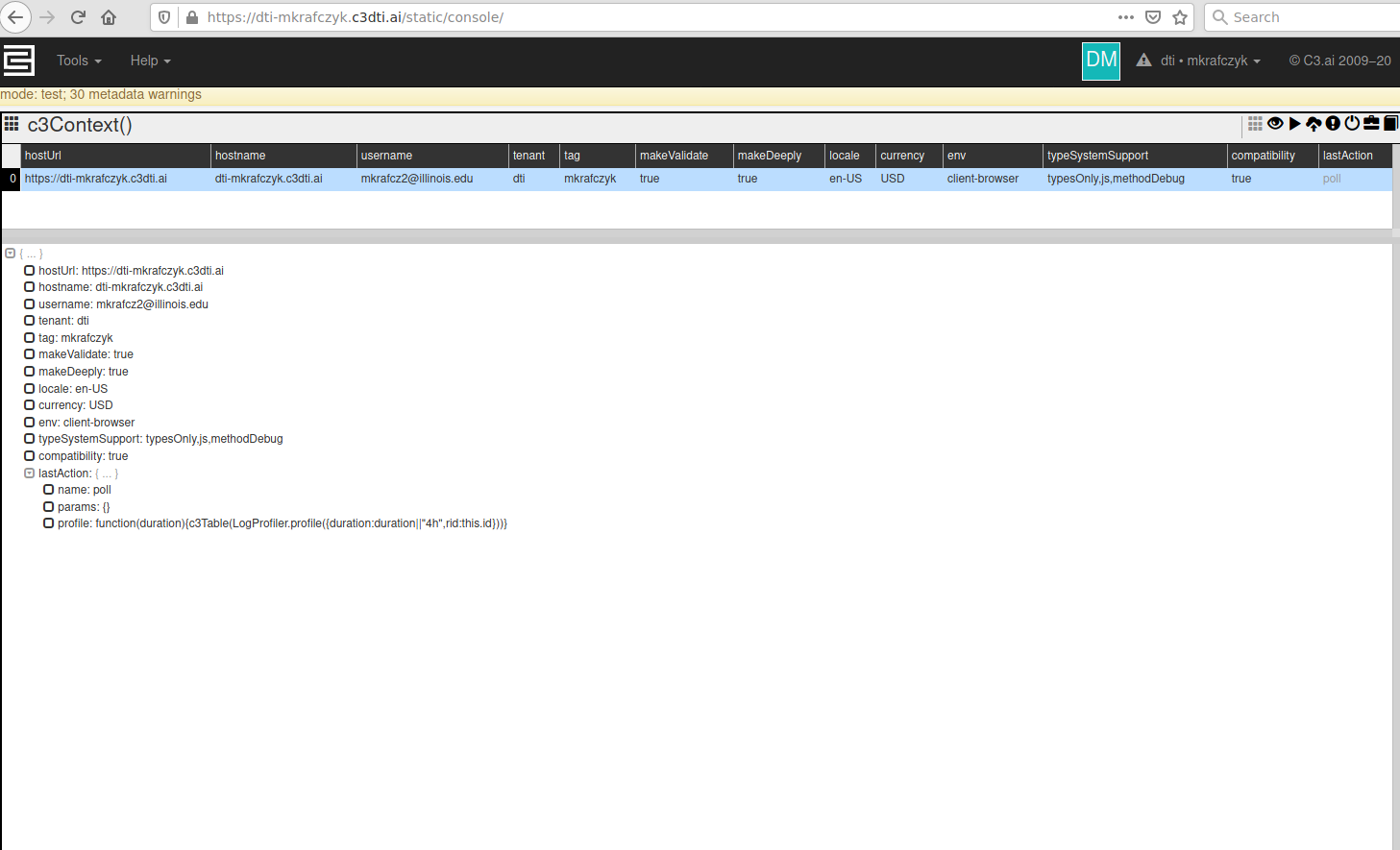
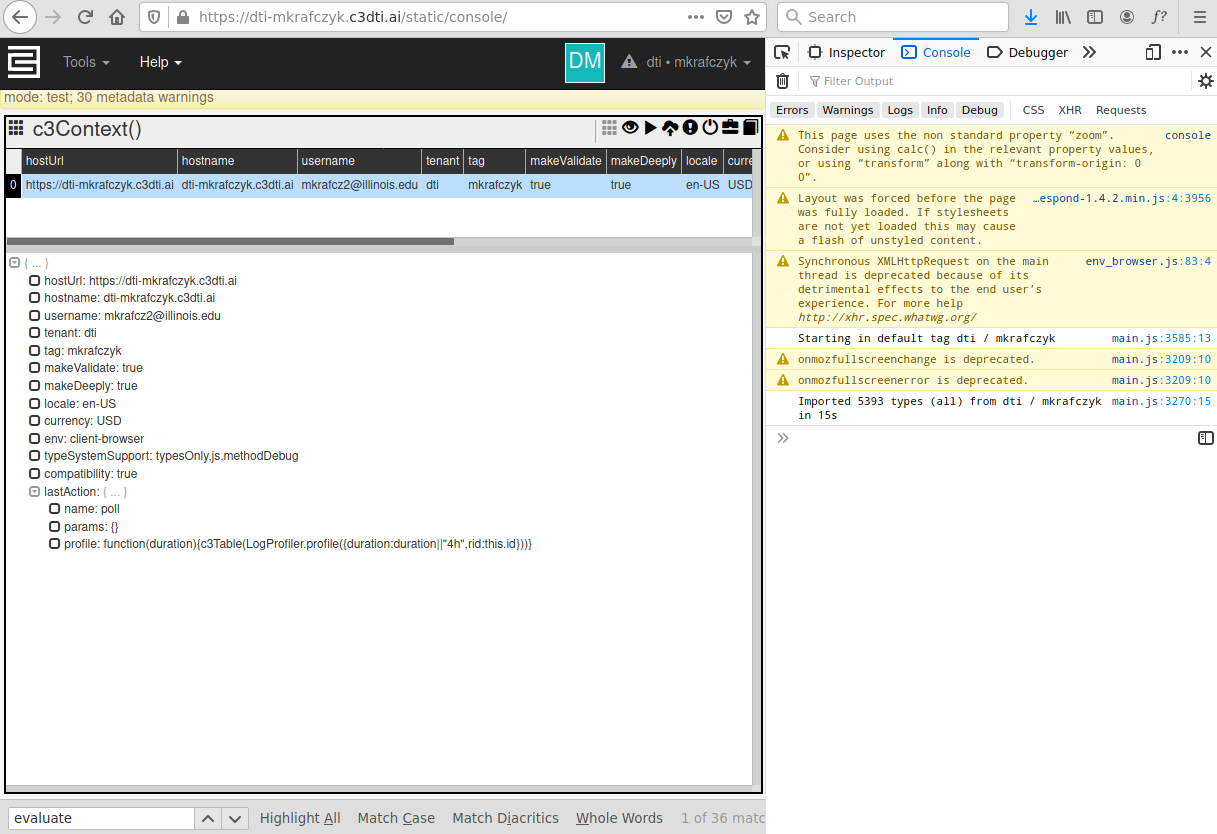
Once your C3 package has been provisioned to your Tenant/Tag, Navigate you have provisioned a package to your tag, navigate to the static console page . This is at this url: 'https://<vanity_url>/static/console' (Replace replacing <vanity_url> with your vanity url., e.g., https://dti-mkrafczyk.c3dti.ai/static/consoleyour Vanity Url provided in your C3.ai DTI Training Cluster Onboarding Email). The static console page looks like this:
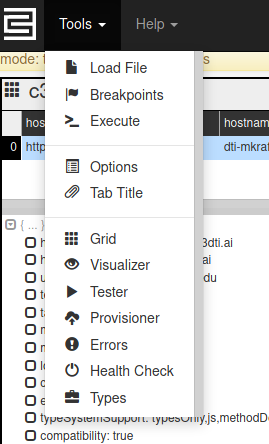
The 'Tools' drop-down menu in the upper left-hand corner contains a menu to access some available list of available developer tools. Most The most relevant tool is the Provisioner, though there are also utilities for loading JavaScript files, debugging JS code, and inspecting Errors.
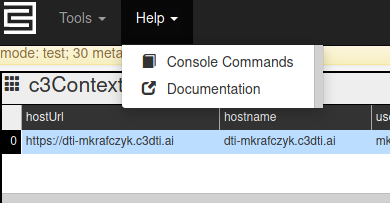
The 'Help' drop-down menu in the upper left-hand corner contains a quick menu allows users to access console documentation and a C3 Cluster hosted documentation portal.
Additionally, most Most tools are also accessible through a series of icons in the upper right-hand corner with a series of Icons:
Using the Static Console
Once you're at Developers interact with the static console , the primary method of interaction is through the JavaScript console of your tab in the browser. When the static console page loads (or when you run the c3ImportAll() command), JavaScript methods associated with all of your Package's defined Types are populated. This allows you to You can write and run JavaScript code right directly in the console tab to interact with your C3 Packagepackage.
Most browsers use the keyboard shortcut You can also open Javascript console with the 'Ctrl+Shift+I' to open the JavaScript console. It is also usually keyboard shortcut (in most browsers). Javascript console is also available through the browser's developer tools. If the 'Ctrl+Shift+I' keyboard shortcut doesn't work for you, look at your browsers documentation for the review your browser's documentation on developer tools. With the JavaScript console open, the static console looks like this on the Firefox browserHere's how the static console looks in Firefox, with the JavaScript console open:
Finally, we can enter let's write some JavaScript code commands to see the console in action!
Console Commands
We review here several highly used JavaScript console commands which are available on the static console page.
Tutorial Video
The DTI Team have recorded a short video introducing and describing the static console functionality:
| Multimedia | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Console Commands
Here are common JavaScript console commands used on the static console page.
- c3ImportAll: A console command which loads all the C3 Types from your package into the static console. Always be sure refresh the static console page or run
c3ImportAll()after provisioning a new packagec3ImportAll: A console command which loads the API of the current C3 Package. This is necessary after provisioning a new Pacakge if you haven't refreshed your static console page. - c3Grid: A console command to display a table of data contained stored within a C3 Type. (e.g., data returned from a fetch operation, or an evaluate operation among many others).
- c3Viz: A console command which can to produce quick visualizations of or plots for some C3 Types. (e.g., timeseries time-series data like
EvalMetricsResult) - c3ShowType: A console command which produces to access documentation about for a given typeC3 Type. (e.g.,
c3ShowType(OutbreakLocation))
Official C3
...
AI Training Materials on Static Console
- Developer Documentation
- C3.ai Academy Videoshttps://learnc3.litmos.com/course/3802340/module/7466371/Scorm?LPId=118058
- Console Overview
- Console Orientation
Using Python with the C3 AI Suite
We anticipate most DTI researchers will want to use Python for data analysis. There are two options to connect to a C3 .ai Cluster via Python. Please follow the links below for detailed information about each.
To learn more about the general structure of a C3 cluster, please see the C3.ai resources here:
- Developer Documentation
- https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.1725/guide/guide-c3aisuite-basic/ds-home
- https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.1725/guide/guide-c3aisuite-basic/ds-python-apis
- https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.1725/guide/guide-c3aisuite-basic/ds-home
- https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.1725/guide/guide-c3aisuite-basic/ds-jupyter-notebooks
- https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.1725/guide/guide-c3aisuite-basic/actionruntime
- C3.ai Academy Videoshttps://learnc3.litmos.com/course/3802623/module/7566724/Scorm?LPId=118105
- Python APIs
- Python Runtimes
Fetching Instances of C3 Types
All data in the C3 AI Suite are stored in C3 .ai Types. Users can access data from a C3.ai Type Type with the 'fetch' method. Behind the scenes, the 'fetch' method submits a query directly to the database underlying a C3.ai Type, and retrieves and presents the query results to C3 AI Suite users.
The C3 AI Suite returns the 'fetch' query's response, which includes (1) :
- data from the
...
- Type itself;
...
- Metadata for the '
fetch' query (e.g., the number of objects, whether additional data exists in the database) into theFetchResulttype
...
- for data analysis (see example below).
To learn more about the 'fetch' method, please see the C3 .ai AI resources here:
- Developer Documentation
- Fetching and Filtering: https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.025/topic/tutorial-fetching-and-filtering
- Fetch and Filter Basics: https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.025/topic/console-data-exploration-fetch-and-filters
- Fetch and Filter Advanced: https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.025/topic/console-fetch-and-filters-advanced
- C3.ai Academy Videoshttps://learnc3.litmos.com/course/3802340/module/7466371/Scorm?LPId=118058
- Fetch & Filters
Users can also provide a FetchSpec (or parameters) to the 'fetch' method to describe particular data to retrieve (e.g., only retrieve gene sequences collected in Germany). The FetchSpec can be 'empty' (e.g., OutbreakLocation.fetch()), or contain several parameters to return a subset of the data.
Some example FetchSpec parameters include:
- filter: Filter expression to return a subset of the data (e.g., age <= 20). Filter expressions must evaluate to a Boolean type (i.e., true or false)
- limit: the The maximum number of rows that should be returned. Be default, if no limit is specified, the C3 AI Suite returns 2,000 rows from the C3 .ai Type. Specifying a limit is often helpful to debug a fetch '
method' , without returning too many records. - include: Specifies the particular fields from a C3 .ai Type to return to the FetchResult. By default, if no
includespec is defined, all fields from the C3.ai Type will be returned. - order: Specifies the order to return the query's results (either "ascending" or "descending").
Note: Please see this C3.ai Developer Documentation for the official FetchSpec documentation for a full list of FetchSpec parameters: https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.17/type/FetchSpec
Examples of Fetch Calls
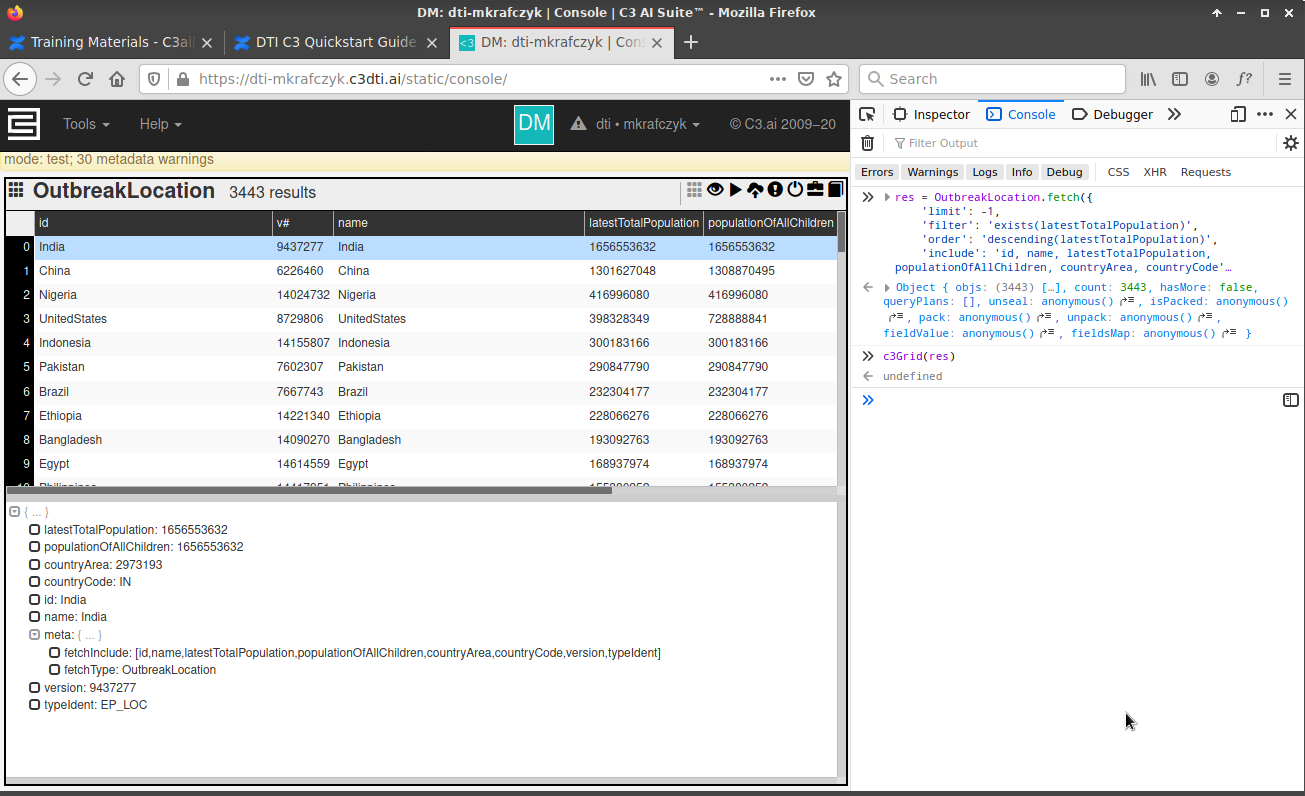
The OutbreakLocation Type contains information from various locations for which the Covid-19 DataLake Data Lake has virus-related information. We can fetch OutbreakLocation records , for which the 'latestTotalPopulation' field exists (i.e., is not null). We can also retrieve these records in descending order by their 'countryArea'.:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
res = OutbreakLocation.fetch({
'limit': -1,
'filter': 'exists(latestTotalPopulation)',
'order': 'descending(latestTotalPopulation)',
'include': 'id, name, latestTotalPopulation, populationOfAllChildren, countryArea, countryCode'
}) |
And we can show these results in the C3 AI static console using the c3Grid command.:
You can run this same fetch in Python:
...
Additional details on "Fetching in Python" are available in this C3 .ai AI Developer Documentationdocumentation: https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.025/topic/ds-jupyter-notebooks
Additional examples of fetch calls can be found in our examples here:
- https://github.com/c3aidti/casesExample
- https://github.com/c3aidti/genomicsExample
- https://github.com/c3aidti/HouseCoverageExample
- https://github.com/c3aidti/VaccineListing
- https://github.com/c3aidti/EpidemiologyExample
Tutorial Video
This tutorial video goes over fetching and filtering:
| Multimedia | ||
|---|---|---|
|
The fetchCount Method
Another useful fetch command is 'fetchCount. This function is nearly identical to the fetch commands above, but it just '. Like 'fetch', users can also provide a FetchSpec (or parameters) to 'fetchCount'. The 'fetchCount' method then returns the number of records which that match the fetch filterFetchSpec. This is useful when trying to determine whether a given search is refined enough.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
OutbreakLocation.fetchCount({'filter': 'exists(latestTotalPopulation)'}) |
The same You can run the same 'fetchCount' in python is:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
c3.OutbreakLocation.fetchCount(spec={'filter': 'exists(latestTotalPopulation)'}) |
To learn more about the 'fetchCount' method, please see the the fetchCount method definition in the Persistable Type documentation: https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.1725/type/Persistable
Converting Fetch results to usable forms in Jupyter Notebook
When using a Jupyter Notebook, C3 .ai AI developers typically modify FetchResults for data analysis. This section shows a couple of ways to convert FetchResults into easy-to-analyze forms.
Python
In python, first , retrieve the 'objs' field from the FetchResults object, and then call the toJson() function. The The toJson() function returns an array of dictionaries each with keys equal to the requested fields of the fetched C3 .ai Type. Using the Pandas library, this array can be turned into an analysis-ready DataFrame, as the below example shows.A Code Example in Jupyter Notebook:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(raw_data.objs.toJson())
df.head()
df.drop('meta', axis=1, inplace=True)
df.drop('type', axis=1, inplace=True)
df.drop('version', axis=1, inplace=True)
df.drop('id', axis=1, inplace=True)
df.head() |
...
Users can then manipulate the resulting DataFrame, using common programming libraries and frameworks.
ExpressionEngineFunctions
The C3 AI Suite also provides a pre-built library of "ExpressionEngineFunctions". Expression EngineFunctions Engine Functions take a variety of arguments and perform various data processing tasks. For example, the function 'contains' takes two strings as arguments , and checks whether the first argument contains the second argument. The function 'lowerCase' takes as input a string , and returns that same string with all lowercase letters. In addition to these string processing functions, the C3 AI Suite's ExpressionEngine includes many math functions (such as 'log', 'avg', and 'abs', ) which operate on a various input data types (e.g. int, double, float).
The ExpressionEngine Functions are used in several places, such as:
- '
fetch' filters - simple Simple and compound metric expressions
tsDeclmetric values
Please see this C3.ai Developer Documentation for a full list of To learn more about ExpressionEngineFunctions, please see the C3 AI Suite's ExpressionEngineFunctions: resources here:
- Developer Documentation
...
...
- C3.ai Academy Videos:
- ExpressionEngineFunctions
Computations on C3 Types using Evaluate
Using The C3 AI Suite provides the 'evaluate' method to compute simple expressions on the data stored within , developers can run aggregations or other computations on data fetched from a C3 Type. (e.g., compute the average area of across all OutbreakLocations which are countries and for which we have area information)countries with area data available, in the OutbreakLocation Type).
The 'evaluate' method takes several The evaluate function takes the parameters:
- 'projection': [Required] A comma-separated list of valid expressions or ExpressionEngineFunctions to evaluate on the aggregated Type data. Behind the scenes, the C3 AI Suite translates these expressions to necessary SQL queries, but not all ExpressionEngineFunctions can be evaluated in SQL. In these cases, evaluate will try to do this itself, but without other SQL abilities like grouping or ordering.
- 'group': A comma separated list of valid expressions or ExpressionEngineFunctions to evaluate as a group parameter of the SQL query
- expressions (from the ExpressionEngineFunction library) to apply to data from a C3 Type (e.g.,
avg,unique,min,max). You can simply think about a projection as the columns/fields, calculated or otherwise, which the "evaluate" method should return. - group: A comma-separated list of columns/fields, to group the aggregated/transformed data by (e.g, compute the average area by the '
locationType' field inOutbreakLocation). Please note, in any 'evaluate' command, all columns in the 'group' field MUST ALSO BE in the 'projection' field, as the example below shows. - having: A 'having': An SQL style having clause.
- 'order': A comma-separated list of valid expressions or ExpressionEngineFunctions to perform an ordering of the results by
- 'filter': A fetch filter expression which restricts the rows evaluate is run against.
On the static console, using the 'c3Grid' displays evaluate's result nicely:
- columns/fields, to order aggregated/transformed data by. Users can access data in 'ascending' or 'descending' order. Please note, in any '
evaluate' command, all columns in the 'order' field MUST ALSO BE in the 'projection' field. - filter: A filter expression that restricts the rows in a C3 Type on which the
evaluatemethod is run.
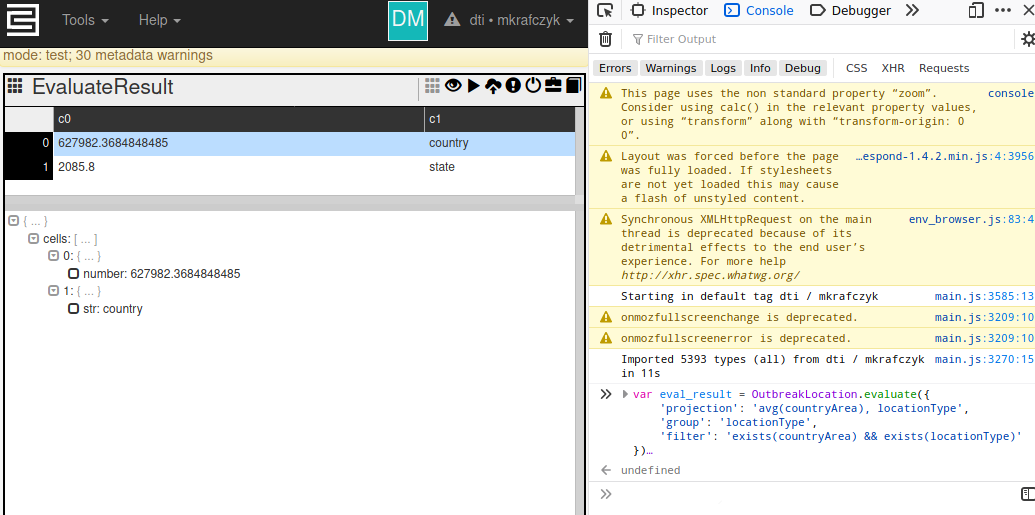
In static console, 'c3Grid' displays the 'evaluate' method results nicely:
(Note: the 'locationType' expression within the 'group' field is also within the 'projection' field. This is required.)
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
var | ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
var eval_result = OutbreakLocation.evaluate({
'projection': 'avg(countryArea), locationType',
'group': 'locationType',
'filter': 'exists(countryArea) && exists(locationType)'
})
c3Grid(eval_result) |
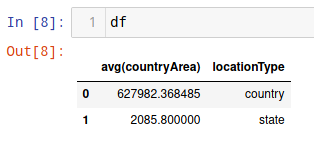
We Users can also use run the 'evaluate' method in Python, but we have to use a helper function. We've defined this for you with the DTI's c3python module available here: https:python. In this case, users often modify the 'evaluate' method's results for data analysis. To view and analyze the 'evaluate' method's results in Python, please use the helper function available in C3 DTI's c3python module here: https://github.com/c3aidti/c3python
NOTE: The 'locationType' expression within the 'group' field is also within the 'projection' field. This is required.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
eval_spec = {
'projection': 'avg(countryArea), locationType',
'group': 'locationType',
'filter': 'exists(countryArea) && exists(locationType)'
}
eval_res = c3.OutbreakLocation.evaluate(eval_spec)
df = c3python.EvaluateResultToPandas(result=eval_res, eval_spec=eval_spec) |
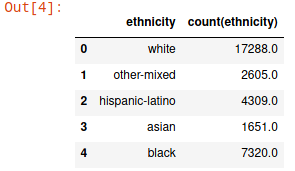
Here's another example of running the 'evaluate' method in Python:, this time using the 'order' parameter as well:
NOTE: The 'count(ethnicity)' expression within the 'order' field is also within the 'projection' field. This is required.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
spec = c3.EvaluateSpec(
| ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
spec = c3.EvaluateSpec( projection="ethnicity, count(ethnicity)", order='descending(count(ethnicity))', group="ethnicity" ) c3python.EvaluateResultToPandas(result=c3.SurveyData.evaluate(spec), eval_spec=spec) |
To learn more about the 'evaluate' method, please see the C3 .aiAI resources here:
- Developer Documentation
...
- 1717
- C3.ai Academy Videos:
- The Evaluate Method
Developing Metrics on Timeseries data
The C3 AI Suite also offers several features to handle timseries time series data. To interact with timeseries C3.ai time series, C3 AI developers typically use simple and compound metrics. These metrics are used in several places in the C3 AI Suite such as:
- Alerts and Application Logic
- Machine Learning Features
- User Interface (to Visualize Data)
Timeseries Video Tutorial
To supplement the documentation below, we also have recorded a video lecture about Time Series data on the C3 AI Platform.
| Multimedia | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Simple Metrics
Simple metrics allow C3.ai developers to produce timeseries time-series from raw data , and are often used to construct more advanced metrics (i.e., Compound Metrics), in practice. Simple metrics are linked to a specific C3 .ai Type and reference the timeseries data stored within that C3.ai Type. To declare a simple metric, users should specify the following fields:
- id: The simple metric's unique id, which should follow the convention "name_srcType" (e.g., Apple_DrivingMobility_OutbreakLocation).
- name: The simple metric's name (e.g., Apple_DrivingMobility).
- description: The simple metric's description (optional field).
- srcType: the The C3 .ai Type the simple metric is analyzed on (e.g.,
OutbreakLocation). - path: The path from the
srcTypeto the C3 .ai Type , that stores the raw data referenced by the simple metric (e.g.,pointMeasurements)
Note: if If thesrcTypeitself stores the raw data referenced by the simple metric, path field is optional. - expression: the The expression (or ExpressionEngineFunction) applied to the raw data, referenced by the simple metric (e.g., avg(avg(normalized.data.quantity)).
Note: the The "normalized" key term , instructs the simple metric to use normalized (instead of raw) data on the C3 AI Suite (to . To learn more about Normalization, see this C3 .ai AI Developer Documentation: https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.1725/topic/normalization ).
Here is an example of a Simple Metric:
...
To learn more about Simple Metrics, please see the C3 .aiAI resources here:
- Developer Documentation
- C3.ai Academy Videoshttps://learnc3.litmos.com/course/3802360/module/7466566/Scorm?LPId=118058
- Metrics
- Simple Metrics
Another type of SimpleMetric is a tsDecl (Timeseries Declaration) metric. tsDecl metrics are often used to turn non-timeseries time series raw data (e.g., event data, status data, or data with irregular intervals) into timeseriestime series. tsDecl metrics have the same fields as standard SimpleMetric, except for the 'tsDecl' field, which replaces the 'expression' field. tsDecl metrics may allow users the added flexibility to define new metrics which that the expression field may not support. Using a a tsDecl metric, the above metric can be re-written as:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
met = c3.SimpleMetric(
id='JHU_ConfirmedCases3_OutbreakLocation',
name='JHU_ConfirmedCases3',
srcType='OutbreakLocation',
path="aggregateMeasurements.(measurementType == 'confirmed' && origin == "
"'Johns Hopkins University')",
tsDecl={
'data': 'data',
'treatment': 'AVG',
'start': 'start',
'value': 'value'
}
) |
To learn more about about tsDecl metrics, please see the C3 .aiAI resources here:
- Developer Documentation
- C3.ai Academy Videoshttps://learnc3.litmos.com/course/3802360/module/7466566/Scorm?LPId=118058
- Time Series Declaration Metrics
Compound Metrics
Compound metrics allow C3 .ai AI developers to manipulate or combine existing metrics into more complex timeseriestime series. Compound metrics are built on top of one or many existing Simple or Compound metrics. Please note, to evaluate a Compound metric on a C3 .ai Type, all Simple metrics , used in that Compound metric , must be defined on that C3.ai Type , as well. OtherwiseIf not, an error is returned.
To declare a compound metric, users should specify the following fields:
- 'id': The compound metric's unique id, typically the same as 'name' (e.g., BLS_UnemploymentRate).
- 'name': The compound metric's name (e.g., BLS_UnemploymentRate).
- description: The compound metric's description (optional field).
- expression: the The expression (or ExpressionEngineFunction) applied to the metrics underlying the Compound metric (e.g., "BLS_LaborForcePopulation ? 100 * BLS_UnemployedPopulation / BLS_LaborForcePopulation: null").
An example CompoundMetric is:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
met = c3.CompoundMetric( id='JHU_CaseFatalityRate', name='JHU_CaseFatalityRate', expression='JHU_ConfirmedDeaths/JHU_ConfirmedCases', ) |
...
To learn more about Compound metrics, please see the C3 .ai AI resources here:
- Developer Documentation
...
- 1717
- C3.ai Academy Videos:
- Compound Metrics
- Compound Metrics
Finding, Evaluating, and Visualizing Metrics
Users can find, evaluate & , and visualize metrics built in the C3 AI Suite , via the JavaScript console or a hosted Jupyter notebook.
Finding Metrics
All metrics that users build and deploy in the C3 AI Suite are also stored in C3 .ai Types. To view a list of all the simple and compound metrics applicable to a C3 .ai Type, run the 'listMetrics' method , as shown below:
Javascript:
...
DTI Members using the Covid-19 DataLakeData Lake: While While listMetrics does return a list, this is fairly bare bones if the 'description' field of a given metric isn't filled in. The Covid-19 DataLake Data Lake API documentation provides an extensive list of production-ready metrics along with detailed descriptions and usage examples. Please see that documentation here: https://c3.ai/covid-19-api-documentation/
After finding a metric, the next step is to evaluate on data in a C3 .ai Type.
Evaluating Metrics
Metrics are evaluated with either the 'evalMetrics' or 'evalMetricsWithMetadata' methods. Behind the scenes, 'evalMetrics' and 'evalMetricsWithMetadata', fetch and transform raw data from a C3 .ai Type into easy-to-analyze timeseries data. 'evalMetrics' is used to evaluate metrics provisioned (deployed) to a C3.ai tenant/tag. 'evalMetricsWithMetadata' allows users to evaluate metrics either provisioned to a C3.ai tenant/tag, or defined on-the-fly in JavaScript console, or a hosted Jupyter notebook (typically for debugging).
To learn more about the differences between 'evalMetrics' and 'evalMetricsWithMetadata' see the C3.ai Developer Documentation documentation here: https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.025/type/MetricEvaluatable
To evaluate a metric, users must provide the following parameters (called an EvalMetricSpec) to the 'evalMetrics' or 'evalMetricsWithMetadata' methods.:
- ids ([string]): A list of ids in the C3 .ai Type , on which you want to evaluate the metrics (e.g., "Germany", "California_UnitedStates").
- expressions ([string]): A list of metrics to evaluate (e.g., "JHU_ConfirmedCases", "Apple_DrivingMobility").
- start (datetime): Start datetime of the time range to be evaluated (in ISO 8601 format) (e.g., "2020-01-01").
- end (datetime): End datetime of the time range to be evaluated (in ISO 8601 format) (e.g., "2020-08-01").
- interval (string): Desired interval for the resulting timeseries data (e.g., MINUTE, HOUR, DAY, MONTH, YEAR).
Here's an example of evaluating a metric in Python:
...
The C3 AI Suite returns the evaluated metric results (a timeseries) into the 'EvalMetricsResult' type. With various helper functions, C3 .ai AI developers may then convert this timeseries into a Pandas DataFrame (via "Dataset" type) for further data analysis or model development in a Jupyter notebook, as shown below.:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
ds = c3.Dataset.fromEvalMetricsResult(result=results) df = c3.Dataset.toPandas(dataset=ds) |
Additionally, users can visualize evaluated metric results directly in the web-browser (i.e., JavaScript console) with the 'c3Viz' function.
Here's an example of evaluating and visualizing in JavaScript console.:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
var spec = EvalMetricsSpec.make({
'ids': ['Illinois_UnitedStates', 'California_UnitedStates', 'UnitedStates' ],
'expressions': [ 'JHU_ConfirmedCases', 'JHU_ConfirmedDeaths' ],
'start': '2020-01-01',
'end': '2020-08-01',
'interval': 'DAY'
})
var results = OutbreakLocation.evalMetrics(spec)
c3Viz(results) |
Similarly, we don't have to explicitly create an EvalMetricsSpec type:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
var results = OutbreakLocation.evalMetrics({
'ids': ['Illinois_UnitedStates', 'California_UnitedStates', 'UnitedStates' ],
'expressions': [ 'JHU_ConfirmedCases', 'JHU_ConfirmedDeaths' ],
'start': '2020-01-01',
'end': '2020-08-01',
'interval': 'DAY'
})
c3Viz(results) |
To learn more about evaluating and visualizing metrics, please see the C3.ai Developer Documentation here:
- https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.17/topic/metrics-evaluating-metrics
- https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.17/topic/metrics-visualizing-metrics
- https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.0/topic/ds-jupyter-notebooks
Note: Metrics can only be evaluated on C3.ai Types that mix in the 'MetricEvaluatable' Type.
Conclusion
Official C3.ai Developer Documentation:
'end': '2020-08-01',
'interval': 'DAY'
})
c3Viz(results) |
To learn more about evaluating and visualizing metrics, please see the C3 AI Developer Documentation here:
- Timeseries Normalization: https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.0/guide/guide-c3aisuite-basic/ts-normalization-engine
- Timeseries Treatments: https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.0/guide/guide-c3aisuite-basic/ts-treatments-home
- Timeseries Metrics:https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.025/guidetopic/guidemetrics-c3aisuiteevaluating-basic/metrics-homeSimple Metrics:
- https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.0/guide/guide-c3aisuite-basic25/topic/metrics-simplevisualizing-metricsCompound Metrics:
- https://developer.c3.ai/docs/7.12.025/guidetopic/guideds-c3aisuite-basic/metrics-compound-metricsjupyter-notebooks
Note: Metrics can only be evaluated on C3 Types that mix in the 'MetricEvaluatable' Type.
Additional Resources
Official C3 AI Developer Documentation:
Review and Next Steps
In For most data analysis, C3 .ai AI developers run the 'fetch' and 'evalMetrics' methods. This C3.ai DTI Quickstart guide provides an introduction to these methods , in which the C3 AI Suite is used as a read-only database , accessed via APIs. In the following guides, you will learn how to run 'write' operations on the C3 AI Suite such as:
- Defining new typesTypes
- Loading new data
- Clean-up databases in your tag
- Train machine learning modelsAnd so on..
Welcome to the start of your experience with the C3 AI Suite.
...