| Table of Contents | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Introduction
This tutorial assumes that you have looked over the Analysis Framework Developer's Guide and have followed the MAEviz development environment tutorial for setting up a development environment. If not, please look at those two documents because this tutorial assumes you have setup your MAEviz development environment and are ready to create a new analysis plug-in so you can begin extending MAEviz.
...
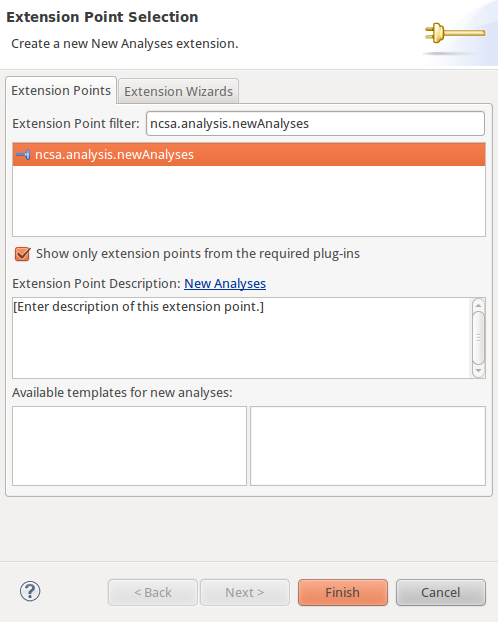
- Click on the Extensions tab and click the Add... button
- In the New Extension wizard that opens, search for ncsa.analysis.newAnalyses, select it and click Finish.
- After adding the extension point, if Eclipse did not add blank new analysis element, right click on the extension point and select New > analysis
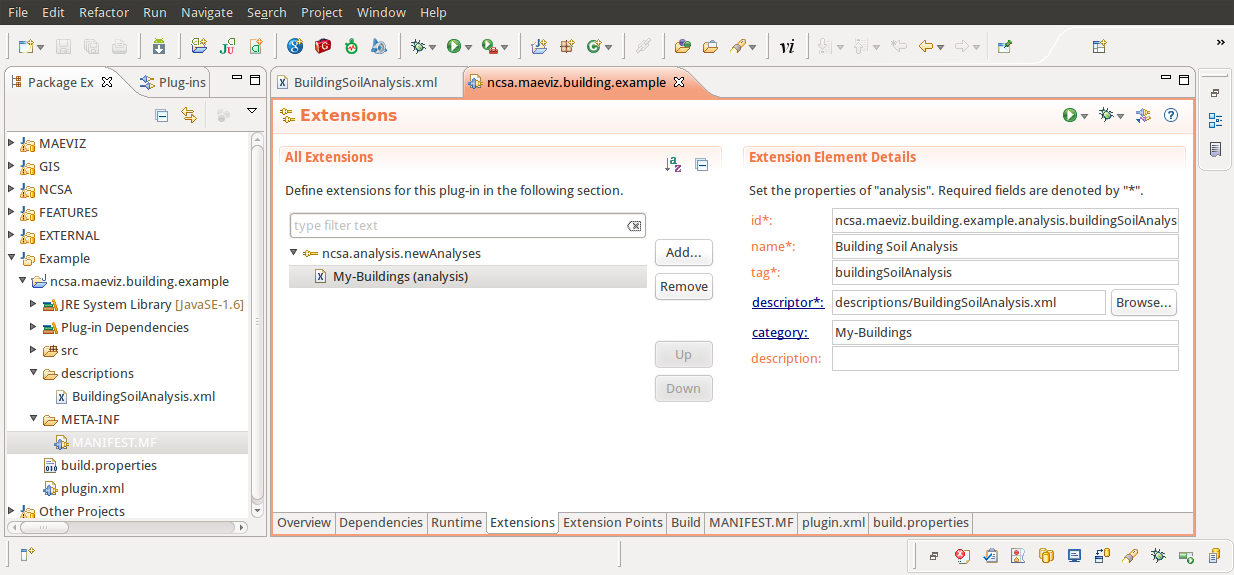
- The next step is to fill in the required parts for the new analysis. Enter the following information
- id: ncsa.maeviz.building.example.analysis.buildingSoilAnalysis
- name: Building Soil Analysis
- tag: buildingSoilAnalysis
- category: My-Buildings
- The final requirement is a descriptor. I recommend creating a new folder inside your plug-in called descriptions and adding a new file called BuildingSoilAnalysis.xml that we will fill in later. After creating this file, you will need to specify it in the descriptor field of your new analysis. You should now have a something similar to the image below:
Your BuildingSoilAnalysis.xml file should contain the following xml statements:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
<analysis-description id ="ncsa.maeviz.building.example.analysis.buildingSoilAnalysis">
<analysis-type type="simpleIteration">
<property name="iteratingDatasetKey" value="buildings">
</property>
</analysis-type>
<groups>
<group-name>Required</group-name>
<group-name>Advanced</group-name>
</groups>
<!-- Analysis Inputs -->
<!-- the result name must be prefixed with the tag of the analysis, in this case buildingSoilAnalysis -->
<parameter format="resultName" phylum="string" cardinality="single" key="buildingSoilAnalysis.resultName" friendly-name="Result Name"/>
<parameter phylum="dataset" cardinality="single" key="buildings" friendly-name="Buildings">
<types>
<type>buildingv4</type>
<type>buildingv5</type>
</types>
</parameter>
<!-- Analysis Outputs -->
<output friendly-name="Building Soil Results" key="buildingSoilAnalysis" phylum="dataset" format="shapefile" geom="buildings" guids="buildings">
<property name="buildings" type="base-dataset-key" value="buildings"/>
<property name="schema" type="schema" value="ncsa.maeviz.building.example.schemas.buildingSoilResults.v1.0"/>
</output>
</analysis-description>
|
Analysis Task
The next step is to create a new analysis task. This is the Java code that will be executed by the new analysis to produce our building soil analysis output. To create a new task, do the following:
...
It is critical that the tag for the Task be identical to the tag for the analysis since this is how MAEviz determines which task goes with which analysis. After entering the text for the class field, if you click on the class, a source file will be generated for you. Where it says Superclass locate the class called SimpleFeatureTask and click Finish. You should see a wizard similar to the one below:
Now that you have your class file, add the missing lines of code from the example below:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
@Override
protected void handleFeature( IProgressMonitor monitor ) throws ScriptExecutionException{
resultMap.put( "soiltype", isSoftSoil() );
}
/**
* Generate a number between 0 and 5 (exclusive)
* 0 - Soil Type A
* 1 - Soil Type B
* 2 - Soil Type C
* 3 - Soil Type D
* 4 - Soil Type E
* @return Soil Type
*/
private int isSoftSoil() {
Random rand = new Random();
return rand.nextInt( 5 );
}
|
Analysis Result Type
The next step is to create a result type schema to specify the new fields created by our analysis. This tutorial will not go into detail about the schema file since it is behind the scope of this tutorial.
...
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsd:schema xmlns:gml="http://www.opengis.net/gml" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" targetNamespace="http://www.ionicsoft.com/wfs" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" xmlns:iwfs="http://www.ionicsoft.com/wfs" targetNamespaceOptionnal="true" xmlns="http://www.ionicsoft.com/wfs" elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xsd:import namespace="http://www.opengis.net/gml" schemaLocation="http://schemas.opengis.net/gml/2.1.2/feature.xsd"/>
<xsd:element name="building-soil-analysis" substitutionGroup="gml:_Feature" type="iwfs:building-soil-analysis"/>
<xsd:complexType name="building-soil-analysis">
<xsd:complexContent>
<xsd:extension base="gml:AbstractFeatureType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="maeviz.soiltype" minOccurs="0" nillable="true" type="xsd:integer"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:extension>
</xsd:complexContent>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:schema>
|
Example Plug-in
You can download the If you have setup your MAEviz development environment, then you should have connected to our Subversion repository. You can find this example plug-in that contains everything in the tutorial by doing the following:by going to the repository at svn://subversion.ncsa.uiuc.edu/ncsa-plugins/ and doing the following:
- Expand trunk
- Find the plug-in ncsa.maeviz.building.example, right click on it and select Checkout.
This will download the plug-in to your workspace. You might need to download this to a new workspace if you already have a plug-in with that project name. Do not overwrite yours unless that is your intent.